How Does a Home Generator Work

Home generators work by converting fuel into electricity, ensuring your home has power during outages. They use engines powered by gasoline, propane, or natural gas to run a generator. When the main power goes out, an automatic switch turns on the generator. This standby generator then supplies power to your home or specific circuits. Once power is restored, the transfer switch turns off the generator and switches your house back to the utility grid. This seamless process ensures that your essential appliances continue running, providing comfort and security during outages. Regular maintenance, such as oil changes and inspections, keeps the generator reliable for emergencies.
Imagine never having your daily routine disrupted by a power outage. Whole house generators are designed to ensure that you and your family stay unaffected by power interruptions, keeping your essential appliances running smoothly. In this article, we’ll dive into how these home generators work and explore their importance and functionality in maintaining your home’s power supply.
What is a Home Generator?
A home generator is a backup power system that automatically activates during a power outage, ensuring that your house remains powered and functional. These systems continuously monitor the electrical current from the utility line. When the generator detects an interruption or failure in the power supply, it starts automatically within seconds, providing electricity to your home.
The generator typically runs on natural gas or propane, reliable fuel sources that can keep the system operational for extended periods. It is connected to a transfer switch, which shifts the electrical load from the utility line to the generator, seamlessly restoring power to your house.
How Home Generators Work
Home generators automatically detect power failures and start up within seconds, providing continuous electricity. Here’s a simple breakdown of how they work:
- Power Outage Detection: The generator system includes a transfer switch that constantly monitors the power coming into your house. When it detects an outage, it signals the generator to start.
- Automatic Start-Up: Once the generator receives the signal, it kicks on automatically, usually within seconds. You don’t have to do a thing!
- Power Generation: The generator, typically fueled by natural gas or propane, begins to produce electricity. It generates power for your essential devices, such as refrigerators, heating and cooling systems, lights, and medical equipment.
- Transfer of Power: The transfer switch disconnects your house from the main power grid and connects it to the generator. This seamless transition ensures your home remains powered without any interruption.
- Restoring Power: When the main power grid is restored, the transfer switch reconnects your house to the grid and shuts down the generator. The generator then goes into standby mode, ready for the next outage.
Home generators provide peace of mind by ensuring your house stays safe, comfortable, and functional, no matter the weather or grid issues.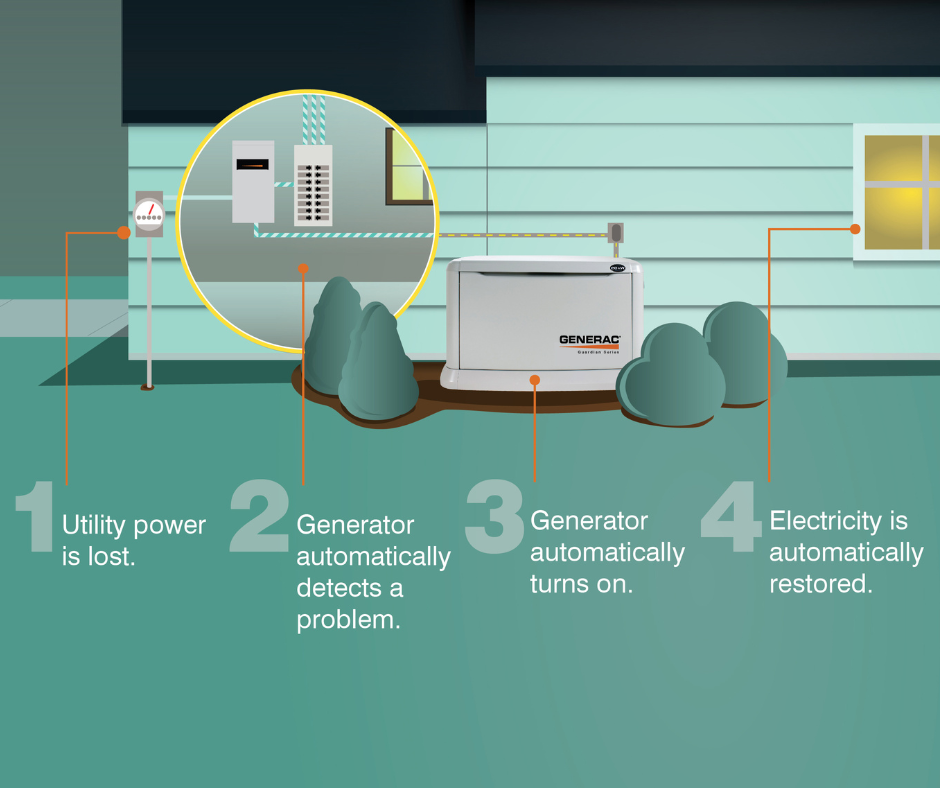
Generators are typically installed in specific locations around your house to ensure optimal performance and safety:
- Outdoor Location: Most home generators are installed outdoors to avoid the risk of carbon monoxide buildup inside the house. Common locations include the side or rear of the house, on a concrete pad or gravel base. This placement allows for proper ventilation and minimizes noise disruption.
- Near the Utility Connection: To make the connection to your home’s electrical system more efficient, generators are often installed close to the main utility connection. This proximity helps reduce the length of wiring needed and ensures a quicker transfer of power.
- Away from Windows and Vents: It’s important to place the generator away from windows, vents, and other openings to prevent exhaust fumes from entering the house. Proper clearance around the generator is also necessary for maintenance and safe operation.
- On a Level Surface: The generator should be installed on a level surface to ensure stability and prevent potential operational issues. Uneven ground can affect the generator’s performance and longevity.
- Accessibility for Maintenance: Ensure the generator installation site allows easy access for routine maintenance and repairs. A clear path to the generator helps technicians perform necessary upkeep without obstruction.
Benefits of Home Generators
- Uninterrupted Power Supply: One of the primary benefits of having a home generator is the uninterrupted power supply it provides. During severe weather conditions, such as hurricanes or storms, or unforeseen power grid failures, a whole house generator ensures that your essential appliances, heating and cooling systems, and security devices remain operational. This means you can continue your daily activities without any disruption, whether it’s working from home, preserving food, or maintaining a comfortable living environment.
- Increased Home Value: Installing a home generator can significantly increase your house’s value. Potential buyers often see the investment in a backup power system as a valuable addition, providing security and convenience. A house equipped with a generator is considered more resilient and attractive, especially in areas prone to frequent power outages. This added value can be a deciding factor for buyers looking for properties that offer greater safety and stability.
- Peace of Mind During Power Outages: A standby generator offers unparalleled peace of mind during power outages. Knowing that you have a reliable backup system in place alleviates the stress and anxiety associated with unexpected blackouts. You won’t have to worry about food spoilage, interrupted work, or losing connectivity. Instead, you can rest easy, confident that your home will remain powered and your family safe, regardless of external circumstances.
Choosing the Right Generator
Selecting the perfect generator for your house involves careful consideration of several key factors to ensure it meets your specific needs and preferences:
- Power Needs (Wattage): The first step in choosing a home generator is determining your power needs. Calculate the total wattage required by identifying all the essential appliances and systems you want to power during an outage. This might include your refrigerator, heating and cooling systems, lights, and any medical equipment. Knowing your power needs helps you select a generator that can handle the load without overloading or underperforming.
- Budget: Budget is a critical factor in your decision-making process. Generators come in a wide range of prices, from basic models to high-end systems with advanced features. Establish a budget that aligns with your financial situation while ensuring you don’t compromise on essential features and reliability. Remember, a higher upfront investment in a quality generator can save you from costly repairs and replacements down the line.
- Fuel Type Preference: Home generators can run on various fuel types, including natural gas, propane, diesel, and gasoline. Each fuel type has its pros and cons:
- Natural Gas: Convenient and often connected to your home’s existing gas line, but may be unavailable during natural disasters.
- Propane: Burns cleanly and has a long shelf life, but requires a separate storage tank.
Choose a fuel type that aligns with your accessibility, storage capabilities, and environmental considerations.
By understanding how home generators work and considering the benefits and factors in choosing the right one, you can ensure your home remains a safe and comfortable haven during any power outage.
Ready to experience the peace of mind that comes with a reliable home generator? Schedule a consultation with one of our Power Consultants today. They will be happy to help you find the perfect generator to meet your needs.


